Property Prediction#
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use TorchDrug to train a graph neural network for molecule property prediction. Property prediction is aimed at predicting the chemical properties of a molecule based on its graph structure and features.
Prepare the Dataset#
We use ClinTox dataset for illustration. ClinTox contains 1,484 molecules labeled with FDA approvment status and toxity status in clinical trials.
Here we download the dataset and split it into training, validation and test sets. The splits for train/valid/test sets are 80%, 10% and 10% respectively.
import torch
from torchdrug import data, datasets
dataset = datasets.ClinTox("~/molecule-datasets/")
lengths = [int(0.8 * len(dataset)), int(0.1 * len(dataset))]
lengths += [len(dataset) - sum(lengths)]
train_set, valid_set, test_set = torch.utils.data.random_split(dataset, lengths)
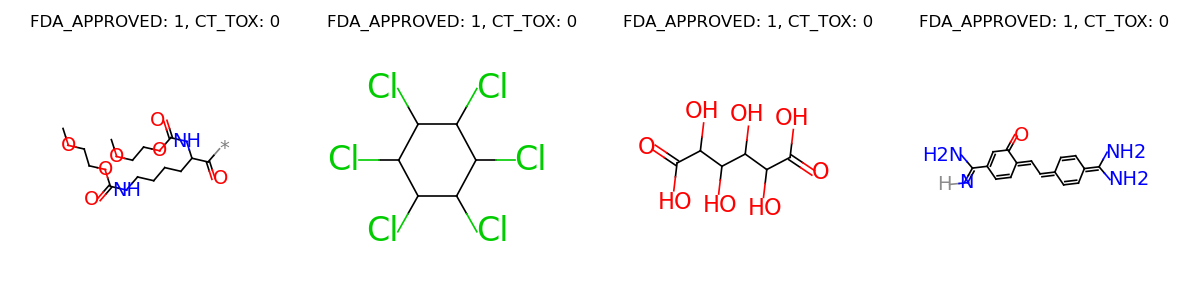
Let’s visualize some samples from the dataset.
graphs = []
labels = []
for i in range(4):
sample = dataset[i]
graphs.append(sample.pop("graph"))
label = ["%s: %d" % (k, v) for k, v in sample.items()]
label = ", ".join(label)
labels.append(label)
graph = data.Molecule.pack(graphs)
graph.visualize(labels, num_row=1)
Define our Model#
The model consists of two parts, a task-independent graph representation model and a task-specific module. We define a Graph Isomorphism Network (GIN) with 4 hidden layers as our representation model. The two prediction tasks will be jointly optimized through multi-task training by the task-specific module.
from torchdrug import core, models, tasks, utils
model = models.GIN(input_dim=dataset.node_feature_dim,
hidden_dims=[256, 256, 256, 256],
short_cut=True, batch_norm=True, concat_hidden=True)
task = tasks.PropertyPrediction(model, task=dataset.tasks,
criterion="bce", metric=("auprc", "auroc"))
Train and Test#
Now we can train our model. We setup an optimizer for our model, and put everything together into an Engine instance. It may take a few minutes to train our model.
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(task.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
solver = core.Engine(task, train_set, valid_set, test_set, optimizer,
gpus=[0], batch_size=1024)
solver.train(num_epoch=100)
solver.evaluate("valid")
Once the model is trained, we evaluate it on the validation set. The result may be similar to the following.
auprc [CT_TOX]: 0.455744
auprc [FDA_APPROVED]: 0.985126
auroc [CT_TOX]: 0.861976
auroc [FDA_APPROVED]: 0.816788
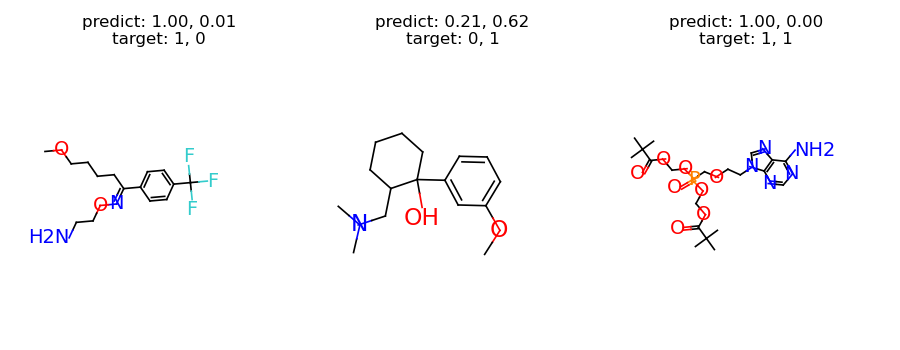
To have some intuition of the model, we can investigate the predictions from our model. The following code selects one sample for each category, and plots the results.
from torch.nn import functional as F
samples = []
categories = set()
for sample in valid_set:
category = tuple([v for k, v in sample.items() if k != "graph"])
if category not in categories:
categories.add(category)
samples.append(sample)
samples = data.graph_collate(samples)
samples = utils.cuda(samples)
preds = F.sigmoid(task.predict(samples))
targets = task.target(samples)
titles = []
for pred, target in zip(preds, targets):
pred = ", ".join(["%.2f" % p for p in pred])
target = ", ".join(["%d" % t for t in target])
titles.append("predict: %s\ntarget: %s" % (pred, target))
graph = samples["graph"]
graph.visualize(titles, figure_size=(3, 3.5), num_row=1)