Deal with References#
As we show in Graph Data Structures, custom graph attributes will be automatically processed in any graph operation. However, some attributes may refer to node/edge/graph indexes, and their values need to be modified when the indexes change. TorchDrug provides a mechanism to deal with such cases.
Inverse Edge Index#
A typical example of reference is a mapping from each edge to its inverse edge. We first prepare an undirected graph with the indexes of inverse edges.
import torch
from torchdrug import data
edge_list = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 2], [2, 1], [2, 0], [0, 2]]
inv_edge_index = [1, 0, 3, 2, 5, 4]
graph = data.Graph(edge_list, num_node=3)
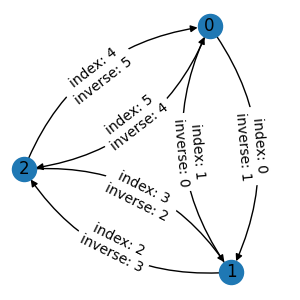
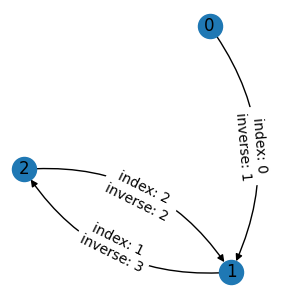
If we assign the indexes as an edge attribute and apply an edge mask operation, the result is not desired. The edges are masked out correctly, but the values of inverse indexes are wrong.
with graph.edge():
graph.inv_edge_index = torch.tensor(inv_edge_index)
g1 = graph.edge_mask([0, 2, 3])
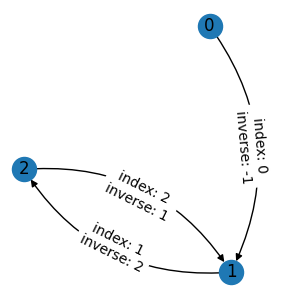
Instead, we need to explicitly tell TorchDrug that the attribute graph.inv_edge_index
is a reference to edge indexes. This is done by an additional context manager
graph.edge_reference(). Now we get the correct inverse indexes. Note that missing
references will be set to -1. In this case, the inverse index of 0 is -1,
since the corresponding inverse edge has been masked out.
with graph.edge(), graph.edge_reference():
graph.inv_edge_index = torch.tensor(inv_edge_index)
g2 = graph.edge_mask([0, 2, 3])
We can use graph.node_reference() and graph.graph_reference() for references
to nodes and graphs respectively.